Scrum
ITEC 4230 Data Science and Analytics Project,
Anca Doloc-Mihu and Cengiz Gunay
(License: CC BY-SA 4.0)

Scrum
* Originally proposed by Jeff Sutherland in 90s, then improved by Schwaber and Beedle
* In 1993, J. Sutherland borrowed term ‘scrum’ from Takeuchi and Nonaka, “The New Product Development Game”, Havard Business Review, 1986
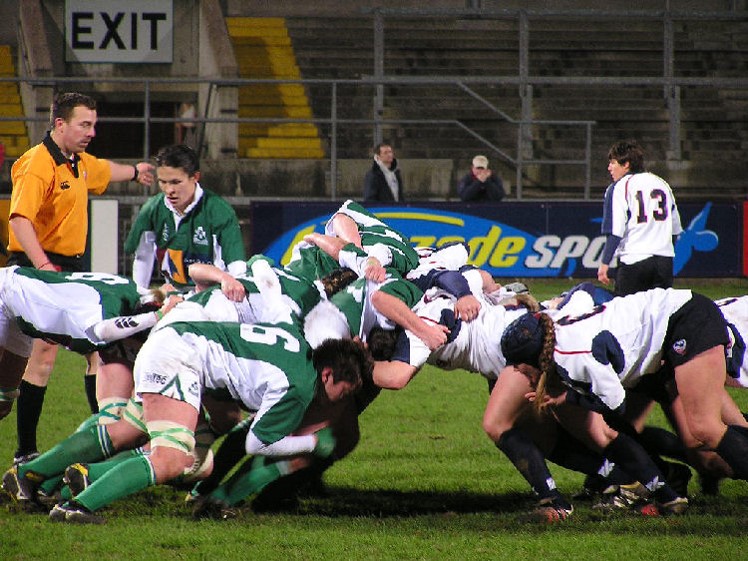
* Takeuchi and Nonaka compare high-performing, cross-functional teams to the scrum formation used by Rugby teams.

Scrum
* In rugby scrum is the power struggle between two teams to advance on the field
* It requires complete team work, hard work, and strength. That meaning translates to software development

See original article from Scrum Alliance
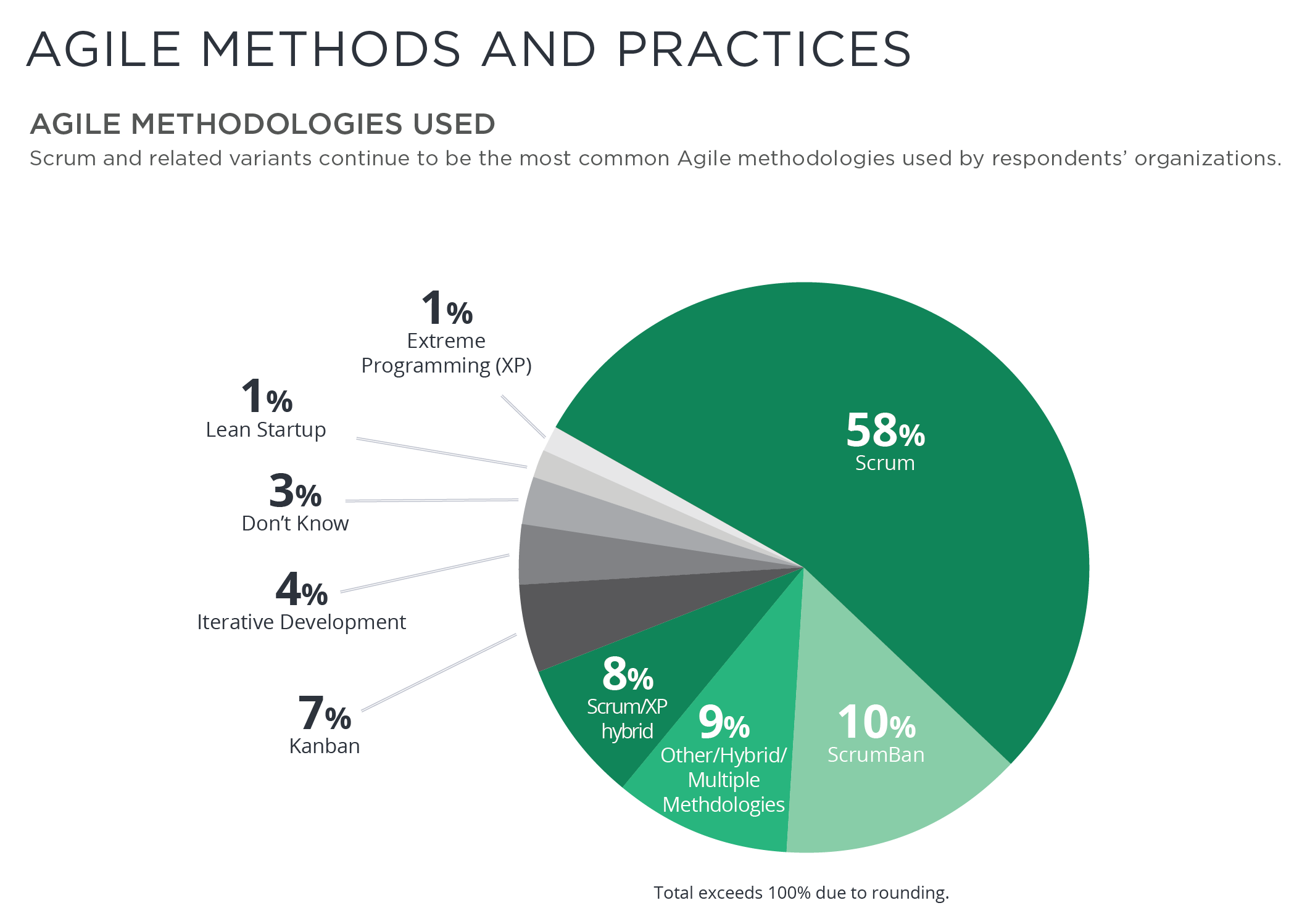
Scrum and Agile
Scrum is one of several agile frameworks.Scrum is the most popular agile framework.
Scrum Definition
Scrum: An [agile] framework within which people can address complex adaptive problems, while productively and creatively delivering products of the highest possible value.
Scrum refers to a lightweight framework that is used in every industry to deliver complex, innovative products and services that truly delight customers. It is simple to understand, but difficult to master.Scrum fulfils the vision of the Agile Manifesto by helping individuals and businesses organize their work to
- maximize collaboration,
- minimize errors,
- deliver frequently, and
- create multiple opportunities to inspect and adapt.
How Scrum works
Scrum works by delivering large projects in small chunks of the product that a team can begin and complete in one, short timeboxed iteration called sprint.
Scrum is also both iterative and incremental.Scrum Framework
People are the focus of Scrum.
Scrum Teams include people with diverse skillsets; each team has all of the capabilities necessary to deliver a piece of functionality from idea to delivery.Sprint is a short (one to four weeks long) timeframe during which the team works on some chunks of the product.
Scrum Team
Scrum Team includes three roles: Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team.
The Scrum Master helps the Scrum Team perform at their highest level. They also protect the team from both internal and external distractions. Scrum Masters hold the Scrum Team accountable to their working agreements, Scrum values, and to the Scrum framework itself.
The Product Owner defines the what–as in what the product will look like and what features it should contain. Product Owner helps build and clarify the product backlog and ensures that everyone knows the priorities.
The Development Team decides how to accomplish the work set forth by the Product Owner. Development Teams are structured and empowered to organize and manage their own work.
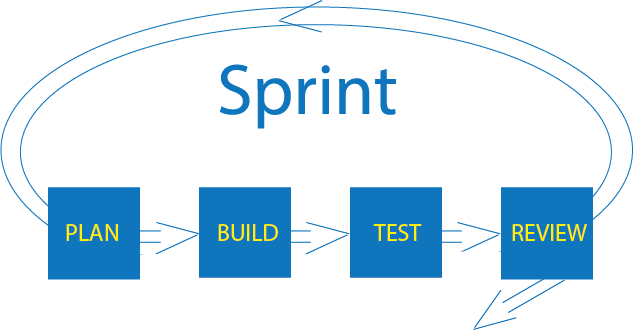
Sprint
Sprint is a short (one to four weeks long) timeframe during which the team works on some chunks of the product.
- Each sprint begins with a plan followed by building and then testing the code, and ends with a review of the work completed and an additional review of the way in which the team worked together (retrospectives).
- During each sprint, the team completes one or more increments of the project. Each completed increment must be fully tested and fully approved by the end of the sprint (potentially deliverable).
Scrum Values
Commitment: Scrum teams work together as a unit, members trust each other to follow through on what they say they are going to do.
Courage: Scrum teams must feel safe enough to say no, to ask for help, and to try new things.
Focus: It means that whatever Scrum teams start they finish.
Openness: Scrum teams consistently seek out new ideas and opportunities to learn.
Respect: Scrum team members respect each other’s ideas, give each other permission to have a bad day once in a while, and recognize each other’s accomplishments. They show respect to one another, to the product owner, to stakeholders, and to the ScrumMaster.
Scrum Artifacts
The Product Backlog is an ordered list of everything that is known to be needed in a product.
The Sprint Backlog is a list of everything that the team commits to achieve in a given Sprint. Once created, no one can add to the Sprint Backlog except the Development Team. If an item needs to be dropped from the Sprint Backlog, they must negotiate it with the Product Owner.
At the end of every Sprint, the team must complete a potentially releasable product increment meaning that it is done as agreed upon.
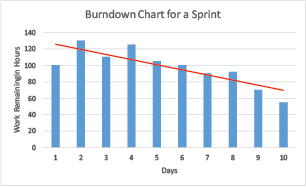
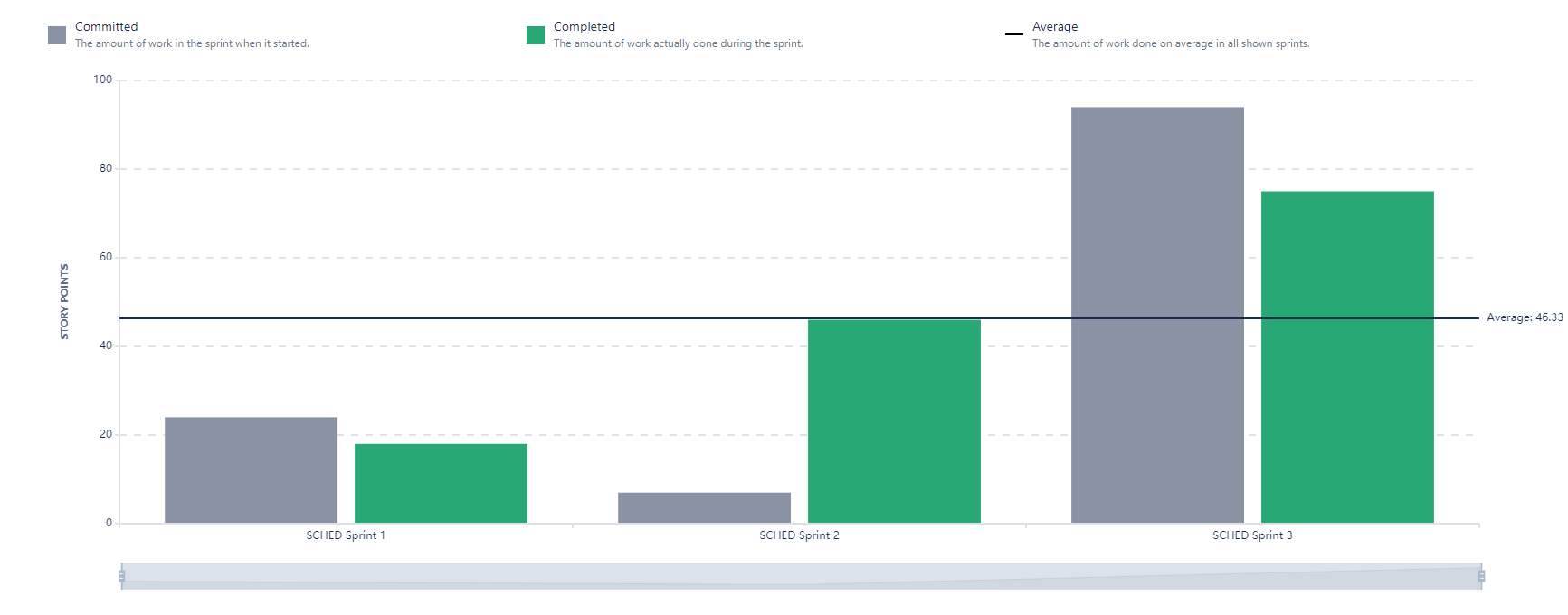
Tracking Progress
Burndown Chart Sprint burndowns are a graphical way of showing how much work is remaining in the sprint, typically in terms of task hours. As the work progresses, the amount of work remaining should steadily decrease and should trend toward being complete on the last day of the sprint.
Daily Scrum
Daily Scrum
What do you see in the clip?
- Scrum Team Members stand up in circle facing everyone. Also, someone else just “observing”. Meeting is less than 15 minutes long.
- Scrum Master Scrum Master starts the meeting. Makes sure everyone talks in order from left to right.
- Each member answers to 3 questions regarding meeting the sprint goal:
1. What did I worked on since last meeting?
2. What I am working on now?
3. Do I see any impediments?
Now … Scrum
Bonus scrum meeting [Sillicon Valey]:
Now … Scrum
